Focus Areas
Focus Areas
Turning Earth Observation into Actionable Environmental Intelligence
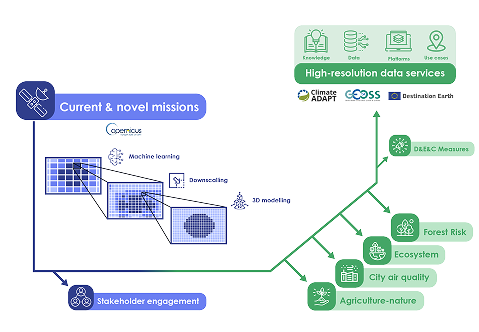
GreenEO develops next-generation satellite-powered tools to tackle Europe's most pressing land-use challenges. Our work is organised into four interconnected focus areas:
Cities & Pollution Reduction, Forest Risk Management, Agriculture & Nature Recovery, and Ecosystem & Biodiversity Monitoring - with Green Governance at the core.
How we work
From Satellites to Policy Impact
GreenEO integrates new satellite missions (Sentinel, EPS-SG, MTG) with models, real-world data, and machine learning to co-develop practical applications with users. Results are delivered as open tools and indicators that support day-to-day decisions.
- Observe: Multi-mission Earth observation + surface observations
- Model: Atmospheric & land models, AI/ML, probabilistic nowcasting
- Deliver: Indicators, maps, and services via a user-friendly portal
- Adopt: Co-design with authorities, agencies, and communities
Focus Area
Cities and Pollution Reduction
Urban areas face some of the highest risks from air pollution, directly affecting the health and wellbeing of millions. GreenEO combines next-generation satellite data with advanced modelling and machine learning to monitor and reduce pollution in cities.
- Sentinel-4: First-ever hourly air-quality observations across Europe; Sentinel-5: global, higher-resolution measurements.
- Integration with other EO instruments, atmospheric models & datasets to map NO₂ and PM₂.₅ from regional down to street scale.
- Up-to-date emission inventories, hotspot detection, and tools disseminated through the GreenEO data portal.
- Co-creation with municipalities, planners, and environmental agencies to ensure direct policy usability and improved quality of life.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂) Concentrations over Europe and Stuttgart in 2019
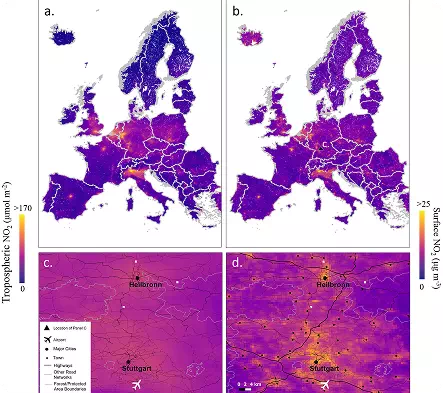
Source: Shetty, S., Schneider, P., Stebel, K., Hamer, P. D., Kylling, A., & Berntsen, T. K. (2024). Estimating surface NO2 concentrations over Europe using Sentinel-5P TROPOMI observations and Machine Learning
Description:
This figure illustrates nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) levels across Europe and the Stuttgart
region in Germany for the year 2019.
Panel (a) presents the annual average tropospheric NO₂ column density measured by
the TROPOMI instrument aboard Sentinel-5P.
Panel (b) shows the corresponding annual mean surface NO₂ concentrations estimated
by the S-MESH machine learning model, derived from daily predictions.
Panel (c) zooms in on the TROPOMI-derived NO₂ column density over Stuttgart, with
the city’s location marked by a triangle in panel (b).
Panel (d) displays the annual spatial distribution of S-MESH-derived surface NO₂
concentrations around Stuttgart, revealing higher NO₂ levels over major urban areas
and along key road networks.
Pilot potential
Urban transport planning, low-emission zones, exposure forecasts.
Expected benefits
- Support for EU Zero Pollution ambition
- Cleaner transport & urban design
- Transparent, citizen-friendly insights
Focus Area
Forest Risk Management
Forests across Europe face growing risks from fires, droughts, and changing climate conditions. GreenEO integrates data from EUMETSAT's new satellites with modelling, surface observations, and artificial intelligence to improve forest risk monitoring and management.
- EPS-SG & MTG satellites: Deliver high-frequency environmental data to capture vegetation and climate dynamics in near real time.
- Fire danger forecasting: Combines satellite observations, meteorological models, and probabilistic approaches (Firelihood) to predict fire likelihood and behaviour.
- New indicators: Introduces fire radiative power (FRP) as a direct measure of fire intensity, integrating fuel moisture and biomass information.
- Operational services: Detects and tracks fires every 15 minutes, forecasts fuel water content, and analyses past trends for improved preparedness.
- User co-creation: Pilot demonstrations with forest management and civil protection agencies in France and Greece, ensuring practical, needs-driven solutions.
Mean Probability of Extreme Wildfire Events in Europe (2020–2024)
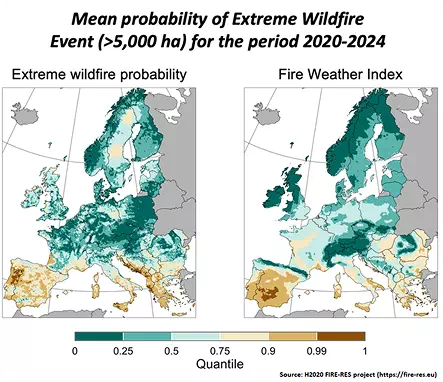
Source: H2020 FIRE-RES project
Description:
The maps illustrate the probability of extreme wildfires across Europe, as estimated
by the INRAE Firelihood tool.
While the Fire Weather Index (FWI) reflects weather conditions conducive to fire, it
alone cannot accurately capture the probability of very large wildfire events,
highlighting the importance of using integrated risk models like Firelihood.
Pilot potential
Co-construction with forest management & civil protection stakeholders in France and Greece.
Expected benefits
- Improved anticipation & preparedness
- Better support for operational services
- Adapted forestry strategies under climate pressure
Focus Area
Agriculture and Nature Recovery
Agriculture plays a central role in Europe's climate transition, but changes in farming practices can impact natural ecosystems and biodiversity through the leaky nitrogen pipeline. GreenEO develops tools and governance approaches to understand and mitigate these effects.
- Data integration: Combines Earth Observation products, in-situ nitrogen measurements, critical load exceedance data, and land cover information to assess impacts on sensitive ecosystems.
- New satellite data: Uses high-resolution observations from IASI-NG (ammonia emissions) together with Sentinels, EPS, and MTG (surface and vegetation characteristics).
- Nitrogen deposition service: Quantifies how agricultural ammonia emissions affect ecosystems through nitrogen deposition — a key driver of biodiversity loss in nutrient-poor habitats.
- Decision support: Provides digital tools to evaluate the sources and sinks of nitrogen and to analyse the cost–benefit of emission-reduction strategies at European scale.
Monthly Mean Leaf Area Index over Europe in 2018-2022 – Open Loop
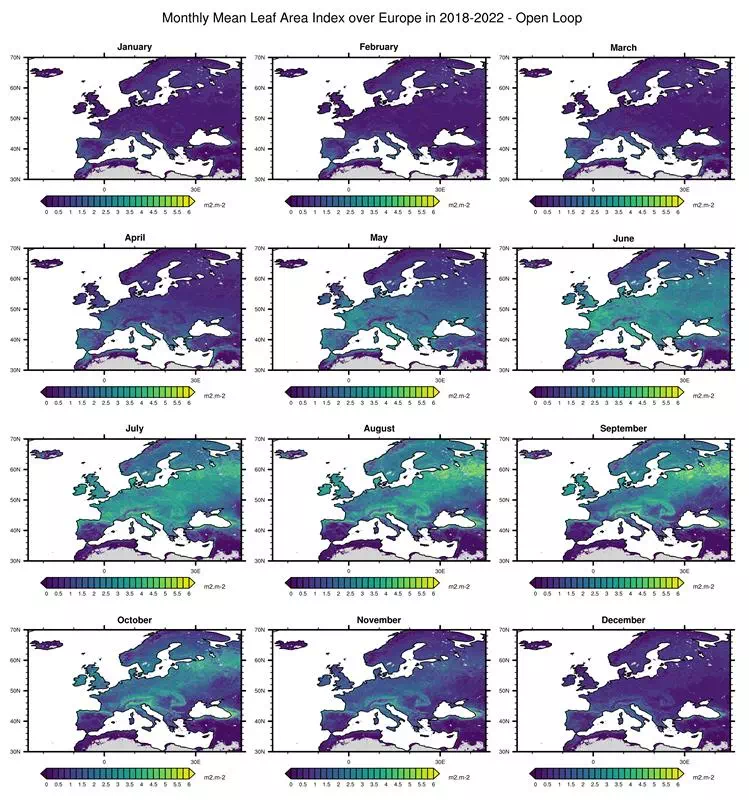
Source: produced during the SEEDS project, courtesy of NILU and CNRM
Description:
The plot is showing monthly averaged leaf area index values over Europe for
2018-2022 calculated with data from the SURFEX land surface model.
Leaf area
index
is a vital part of understanding the impact of nitrogen deposition on vegetation and
nature.
Pilot potential
Assessment of nitrogen deposition impacts on sensitive habitats; Evaluation of emission-reduction measures and restoration potential; Integration with governance and cost–benefit analyses for agricultural transition
Expected benefits
Improved understanding of agricultural nitrogen impacts on biodiversity; Support for evidence-based policies and sustainable land-use planning; Enhanced capacity to balance agricultural productivity with ecosystem recovery
Focus Area
Ecosystem & Biodiversity Monitoring
Healthy ecosystems underpin biodiversity, climate regulation, and human wellbeing. GreenEO combines multi-mission satellite data with modelling and machine learning to track ecosystem condition and biodiversity across Europe.
- Satellite missions: Sentinel, SMOS, SMAP, and next-generation MTG and EPS-SG integrated with advanced modelling/ML.
- High-resolution indicators: Water holding capacity, biomass, and biodiversity.
- Harmonised datasets: Soil moisture, vegetation productivity, and leaf area index (LAI) with improved spatial detail.
- Applications: Carbon stock assessment, forest management, habitat suitability analysis.
- Open platform: Interactive online interface to explore ecosystem conditions at user-defined scales, co-developed with stakeholders.
Soil moisture: an essential piece of the ecosystem platform
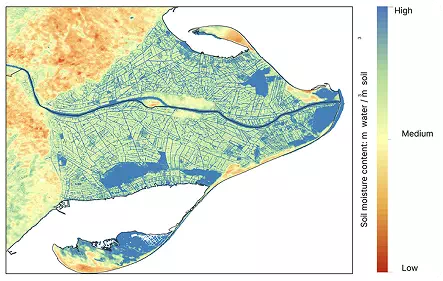
Source: Lobelia
Description:
Satellite soil moisture monitoring in
Catalonia at 30m per pixel in the Ebro Delta in Catalonia, Spain.
Soil moisture is
measured as meters cubed of water/meters cubed of soil. It is an essential Climate
Variable and an early warning signal for drought, providing vital cues as to exactly
where soil is affected.
Pilot potential
Forest certification & ecosystem condition monitoring; Urban renaturing & green infrastructure planning; Natural capital investment & ecosystem accounting.
Expected benefits
Forest certification & ecosystem; condition monitoring; Urban renaturing & green infrastructure planning; Natural capital investment & ecosystem accounting
Green Governance & Use Cases
Integration at the Core
Achieving Europe's Green Deal ambitions requires not only new technology, but new ways of governing environmental change. GreenEO is developing science-based governance models that connect satellite innovation with policy and decision-making. By combining Earth observation data with policy analysis and stakeholder co-design, GreenEO helps ensure that new satellite services are not only technically advanced but also usable, trusted, and aligned with public priorities.
Through collaboration with policymakers, scientists, industry, and civil society, the project turns data into actionable policy recommendations supporting the Zero Pollution and Biodiversity goals of the EU. Our work explores how data-driven tools can make governance more transparent, participatory, and effective by bridging the gap between research, regulation, and real-world impact. These efforts will lead to policy recommendations and tested models that guide the sustainable uptake of GreenEO applications across Europe.
Expected benefits
- Informed policy : translating Earth observation insights into practical environmental decisions
- Collaborative governance : engaging institutions and industry in co-designing solutions
- Transparency and accountability : strengthening evidence-based policymaking.




